B2.1 Cell Structure IGCSE AID
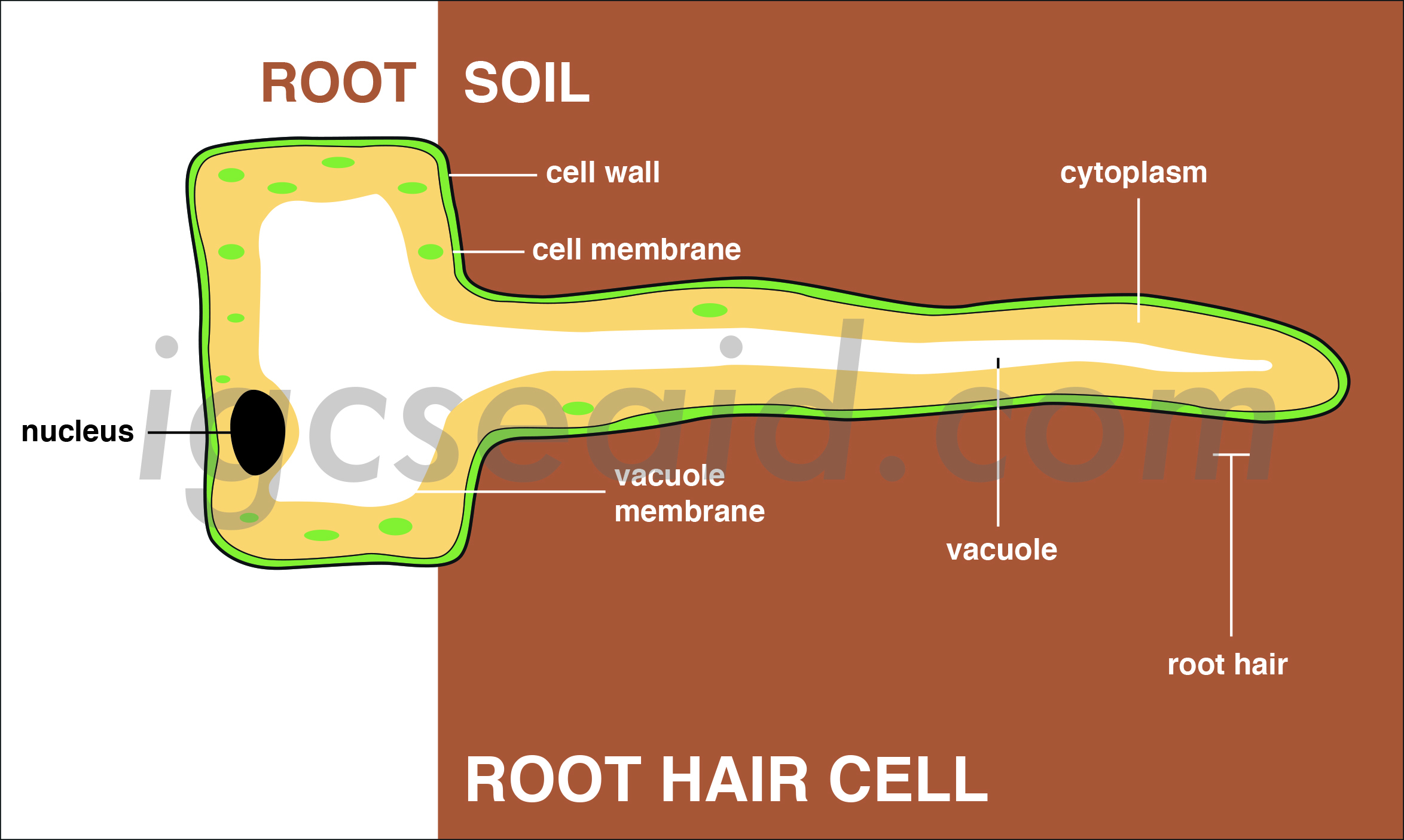
Diagram of the root hair structure Hydrogen is combined with the carbon dioxide to produce the food (glucose) for the plant, whereas the oxygen, which is a by-product of the entire process, is let out through the stomata. If a plant does not absorb enough water, it will wilt or go floppy.

Schematic of the human hair follicle. The hair follicle contains both... Download Scientific
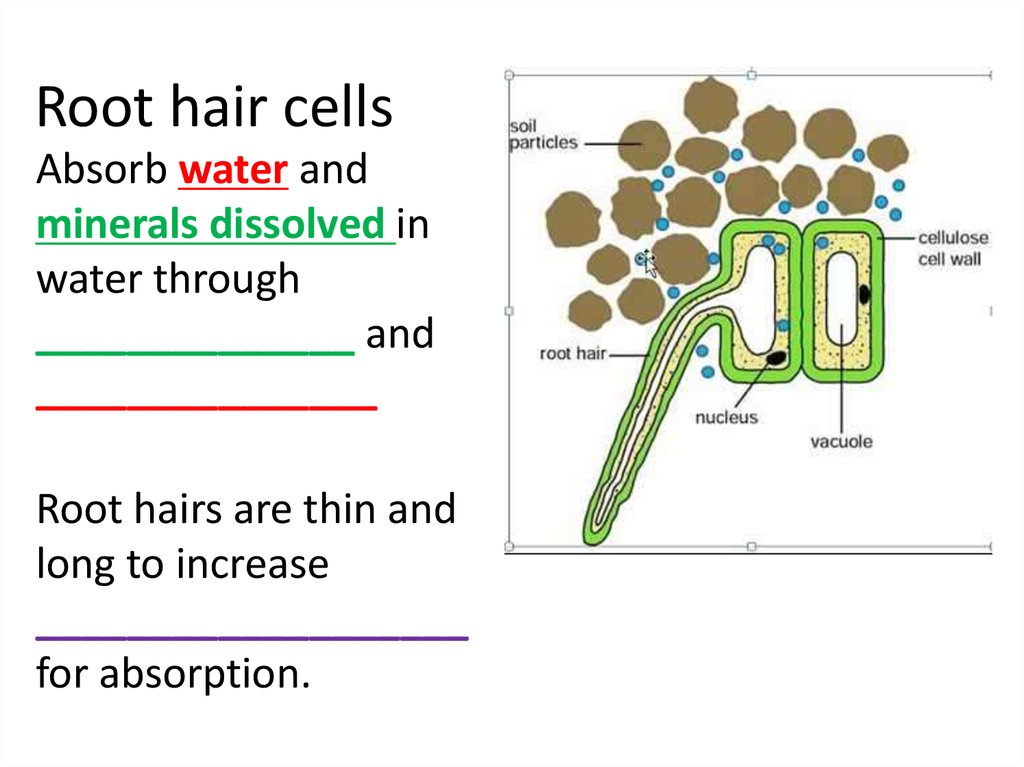
Root hairs are tiny, hair-like structures that grow on the surface of the plant roots. Their main function is to increase the area available for water absorption and that of minerals and other nutrients. Root hairs are delicate structures that can only survive for a couple of days. They do not have the ability to turn into roots.
.PNG)
Tammy Cannon News Roothaircellfromaplantfunction
What are Root Hair Cells? How Root Hair Cells Absorb Water and Mineral Ions From the Soil? Summary of the process Importance of Water for the Plant Water Transport From Root to Leaf Investigating the Water Pathway In this article, we will discuss the root hair cells of the plant in detail.
Maturation Zone Of Root 5 5 The Root Biology Libretexts / Matured cells differentiate into
This lesson demonstrates and explains how substances (water and mineral salts) are absorbed by the root hair cells. Once you are doing photosynthesis and tra.

Tammy Cannon News Roothaircellfromaplantfunction
Introduction Root hair cell is an offshoot of a hair-forming cell of the epidermis. It is mainly considered an exclusive feature of plants, but its contemporary is also found in animal species. The functional unit of root hair cells is recognized as" root hair."

Nutritional Requirements of Plants OpenStax Biology 2e
The dimension of root hair cells ranges between 15-17 μm in diameter and 80-1500 μm in length. The epidermal cells present in the region of maturation of the root are responsible for the growth of root hair. A single root epidermal cell is roughly rectangular with a cytoplasmic extension on its lateral end.

Roothaircellfromaplantfunction
The hair root is in the skin and extends down to the deeper layers of the skin. It is surrounded by the hair follicle (a sheath of skin and connective tissue), which is also connected to a sebaceous gland. New cells are constantly forming in the hair bulb. These cells stick together and harden.
Active Transport In Root Hair Cells Of Plants Transport Informations Lane
Root hair cells Roots hold plants in place as they grow and also absorb water and minerals from the soil. Roots divide into smaller and smaller branches as they travel into the soil. The.

GCSE Biology Root Hair Cell Diagram Diagram Quizlet
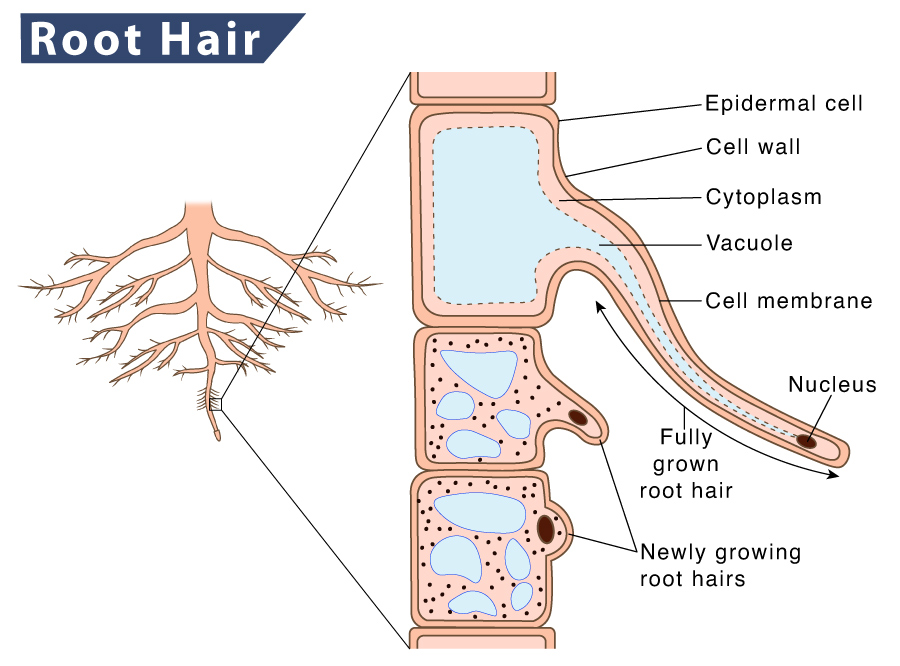
Root hair, or absorbent hairs, are outgrowths of epidermal cells, specialized cells at the tip of a plant root. They are lateral extensions of a single cell and are only rarely branched. They are found in the region of maturation, of the root.

Labelling a root hair cell Diagram Quizlet
The root has an outer layer of cells called the epidermis, which surrounds areas of ground tissue and vascular tissue. The epidermis provides protection and helps in absorption. Root hairs, which are extensions of root epidermal cells, increase the surface area of the root, greatly contributing to the absorption of water and minerals. All three.
Root Hair Cell Function Transport in Flowering Plants Root hair cell root hair cells are
Root Hair Cell Diagram A root hair cell. Root Hair Cells and the Uptake of Water The structure of a root specifically allows it to maximise absorption of water by osmosis and mineral ions by active transport. You've read 1 of your 10 free revision notes Get unlimited access to absolutely everything: Downloadable PDFs Unlimited Revision Notes
a2zPCMB root hair cells
The initial step in the formation of a root hair is the specification of a newlyformed epidermal cell to differentiate as a root hair cell. This represents an example of a central problem in developmental biology; namely, how do particular cell types acquire their identity?

Absorption Of Water
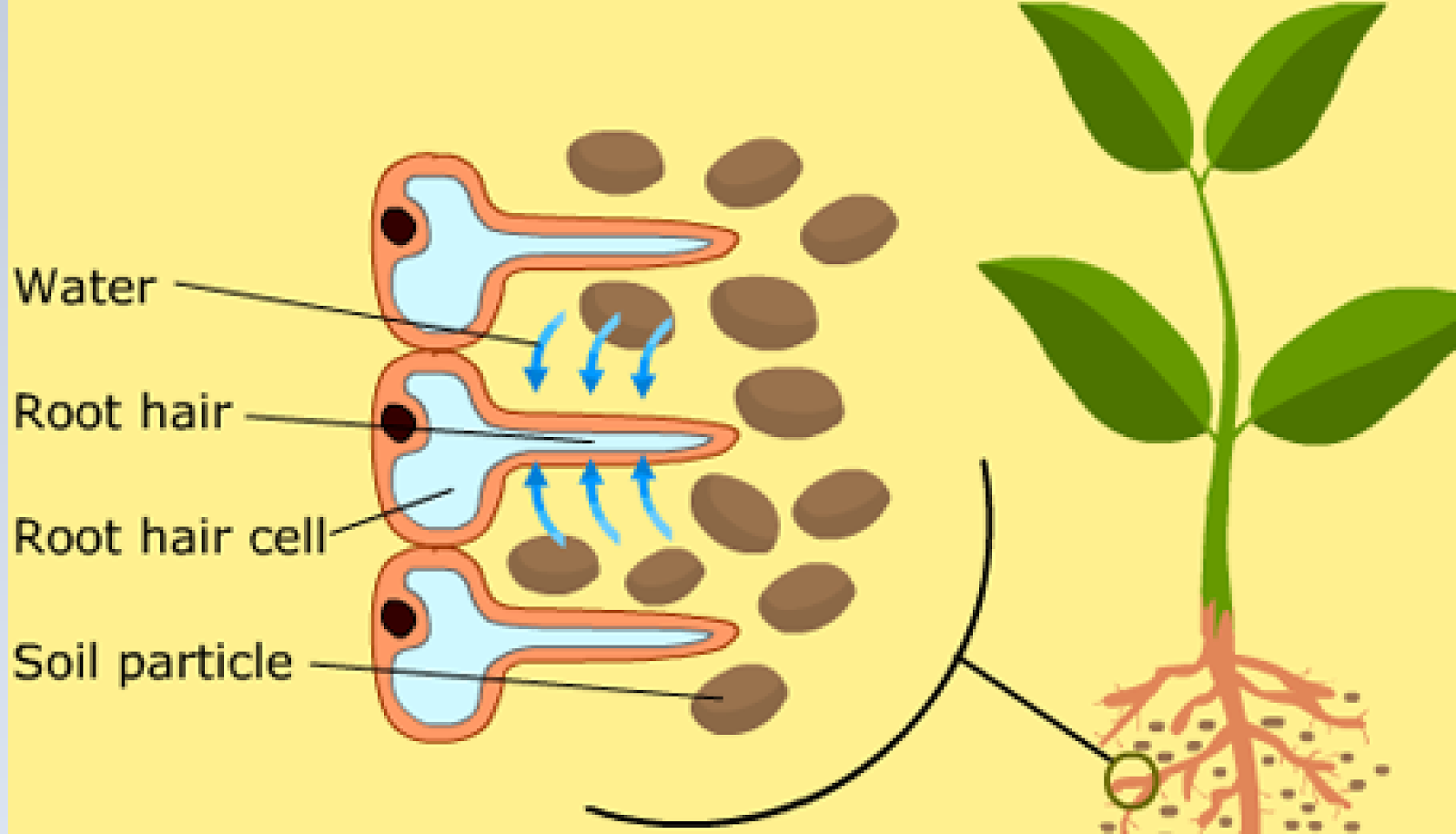
Figure 4.5.1.4.4 4.5.1.4. 4: Movement of water and minerals through the roots. Water moves through the root hairs of the epidermal cells through the cortex, including the endodermis, before entering the outermost layer of the vascular cylinder, the pericycle. the vascular cylinder (stele). Water ultimately enters the conducting cells of the xylem.
Edexcel IGCSE Biology 复习笔记 2.8.3 Water Movement in Flowering Plants翰林国际教育
Root hairs are long tubular-shaped outgrowths from root epidermal cells. In Arabidopsis, root hairs are approximately 10 µm in diameter and can grow to be 1 mm or more in length ( Figure 1 ).
Root Hair Cells Diagram malayakram
Beginning at the first root hair is the zone of cell maturation where the root cells begin to differentiate into special cell types. All three zones are in the first centimeter or so of the root tip. Figure 30.16 A longitudinal view of the root reveals the zones of cell division, elongation, and maturation.
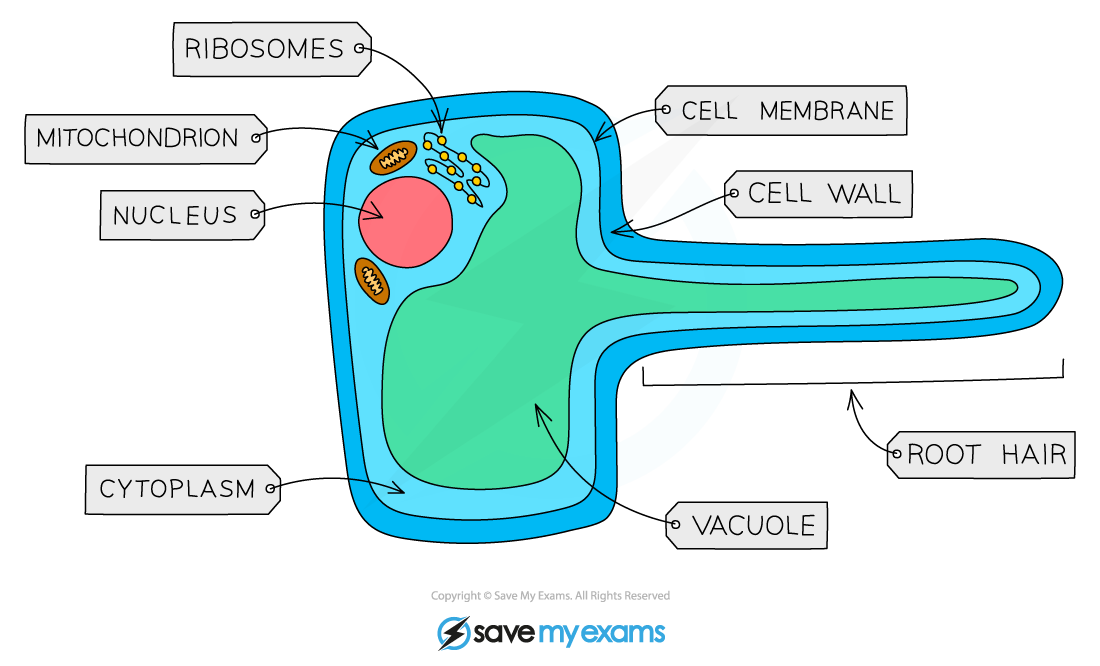
Figure 1.11 The parts of a root hair cell Boost
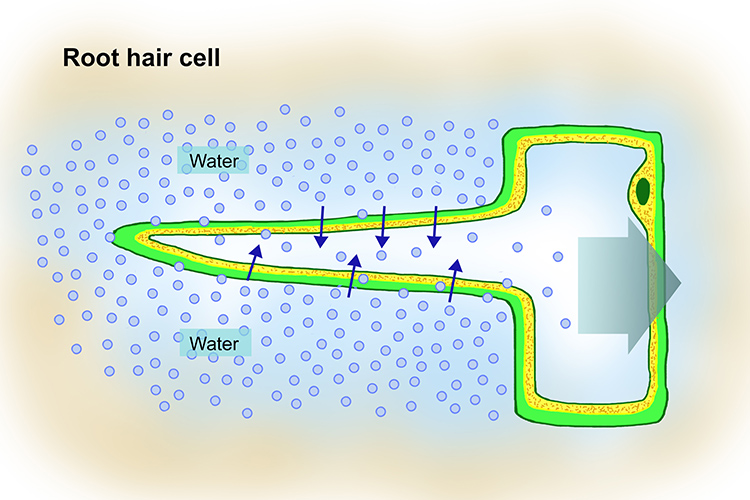
Root Hair Cells. Root hairs are single-celled extensions of epidermis cells in the root. They grow between soil particles and absorb water and minerals from the soil. Water enters the root hair cells by osmosis. This happens because soil water has a higher water potential than the cytoplasm of the root hair cell.